What’s the Difference between Electron Microscopes and Optical Microscopes?
When it comes to scientific research and analysis, microscopes play a critical role in visualizing objects that are too small for the naked eye to see. However, there are different types of microscopes available, each with its unique features and capabilities. In this article, we will explore the difference between electron microscopes and optical microscopes.
What is Optical Microscope?
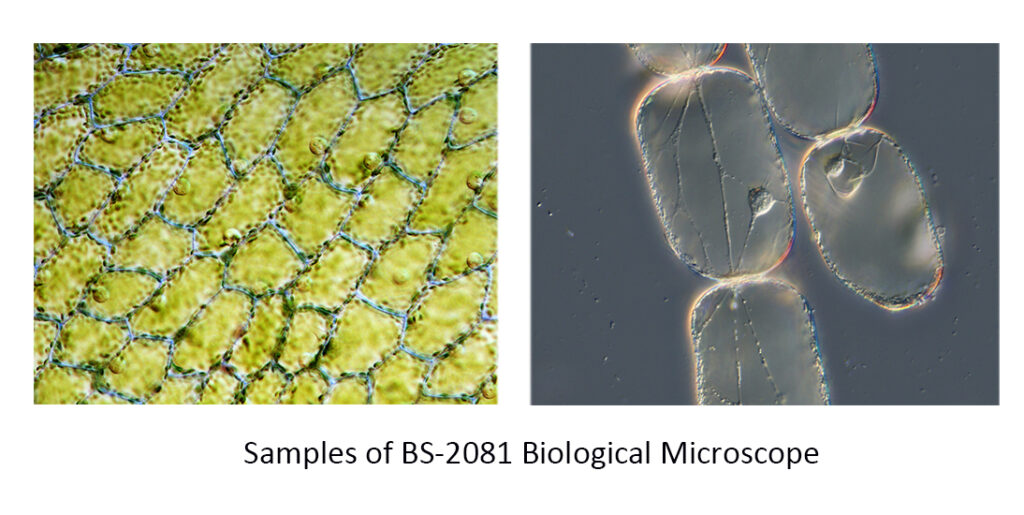
Optical microscopes, also known as light microscopes, use visible light to magnify objects. They work by passing light through a lens, which then magnifies the image. The magnification power of an optical microscope ranges from 40x to 3000x (generally is 1000x), making it ideal for observing living organisms and other small objects.
One of the most commonly used types of optical microscopes is the compound microscope, which uses two or more lenses to magnify the image of a specimen. It is widely used in biology, microbiology, and medical research to study the structure and function of cells and tissues. Other types of optical microscopes include the stereo microscope, which provides a three-dimensional view of the specimen, the polarizing microscope, which is used to study the optical properties of materials, the metallurgical microscope, which is used in high-powered microscopes for viewing opaque objects. (Information Reference: How Many Types of Optical Microscopes?)
Biological Compound Microscope Stereo Microscope
Polarizing Microscope Metallurgical Microscope
The optical microscope is relatively inexpensive, easy to use, and provides high-quality images of specimens. It also allows for the observation of live specimens in real-time and allows for the manipulation of specimens through various techniques such as staining, sectioning, and contrast enhancement. Additionally, the optical microscope has a wide range of applications in various fields such as biology, chemistry, materials science, and forensic science. Therefore, the optical microscope is an essential tool for scientific research.
What is Electron Microscope?
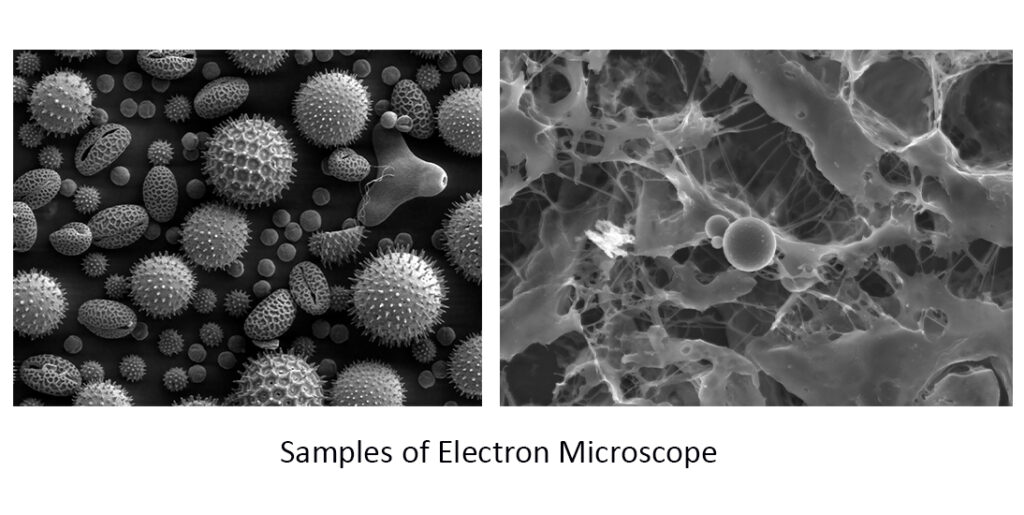
Electron microscopes use a beam of electrons to magnify objects. They are capable of much higher magnification than optical microscopes, with a maximum magnification power of up to one million times. This makes them ideal for studying extremely small objects such as viruses, atoms, and even individual molecules.
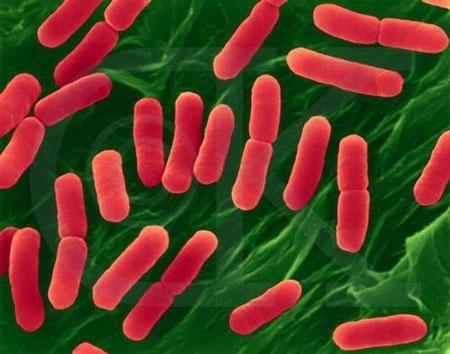
There are two types of electron microscopes: transmission electron microscopes (TEM) and scanning electron microscopes (SEM). TEMs use a beam of electrons to pass through a thin sample, producing a two-dimensional image of the object’s interior structure. SEMs, on the other hand, scan the surface of the sample with a beam of electrons, producing a three-dimensional image of the object’s surface.
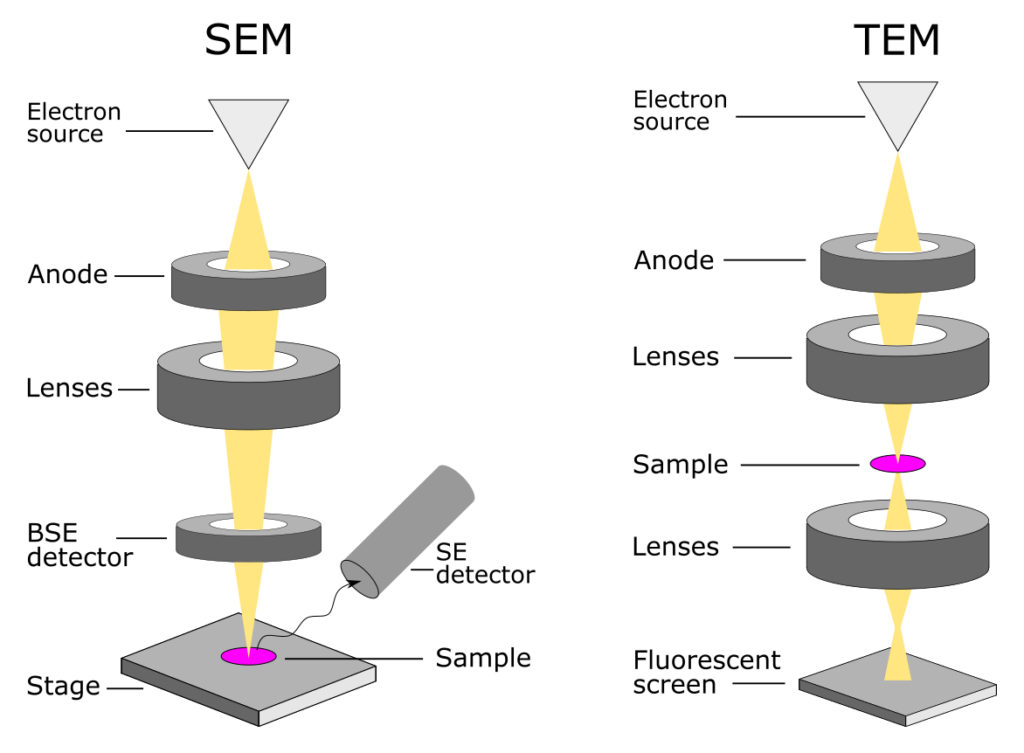
Unlike optical microscopes, electric microscopes require a vacuum to operate as the electrons cannot travel through air. They are also more expensive and complex to use, requiring specialized training and maintenance.
Difference between Electron Microscopes and Optical Microscopes?
|
|
Electron Microscope |
Optical Microscope |
|
Magnification |
Higher magnification Magnify objects up to 1000000X |
Lower magnification than an electron microscope Magnify up to 3000X |
|
Resolution |
High resolution Distinguish objects a few nanometers apart |
Low resolution Distinguish objects a few hundred nanometers apart |
|
Light Source |
Use a beam of electron |
Use visible light |
|
Image Formation |
Use electromagnetic lenses to focus the electron beam and create an image |
Use glass lenses to bend and focus light to create an image |
|
Sample Preparation |
Require the sample to be prepared in a vacuum and coated with a thin layer of metal |
Observe samples in air or liquids without any special preparation |
|
Cost |
Expensive and high maintenance cost |
Inexpensive and requires low maintenance cost |
In conclusion, both optical and electron microscopes have their unique features and capabilities. The choice of microscope depends on the nature of the sample being studied and the level of magnification required. Electron microscopes are better suited for observing very small objects, while optical microscopes are better suited for observing larger objects and for live cell imaging.
The resources are collected and organized on the Internet, and are only used for learning and communication. If there is any infringement, please contact us to delete.